The LFMP/NMC CAM Revolution: A New Era in Battery Technology
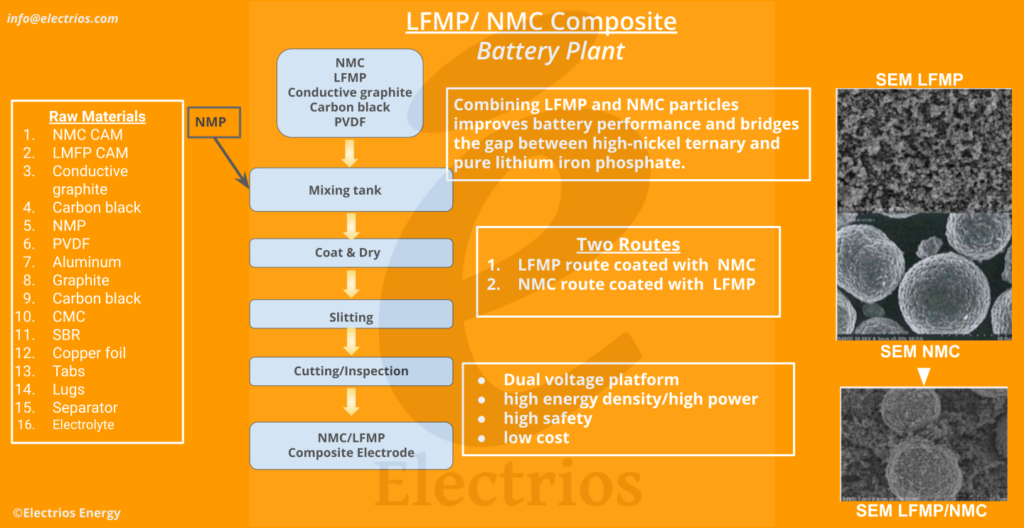
Combining Lithium Ferromanganese Phosphate (LFMP) with NMC particles enhances battery performance across a wide range of applications.LFMP’s large specific surface area and small particle size allow it to effectively fill the gaps between NMC particles or adhere to their surfaces, forming a composite cathode active material (CAM) system.This composite CAM exhibits an energy density that bridges the gap between high-nickel ternary cathodes and pure lithium iron phosphate, offering a compelling alternative for various applications.
The similarities in voltage platforms between LFMP and NMC enable their mixing to address the issue of dual voltage platforms in lithium manganese iron phosphate. Batteries employing composite materials will harness the high energy density and high power characteristics of ternary materials while simultaneously reaping the high safety and low-cost advantages of lithium manganese iron phosphate.
By blending LFMP, known for its poor electrical conductivity, with ternary materials that boast excellent conductivity, the resulting battery with the composite cathode material embodies the high energy density attributes of ternary, as well as the high safety and cost-effectiveness benefits of LFMP.