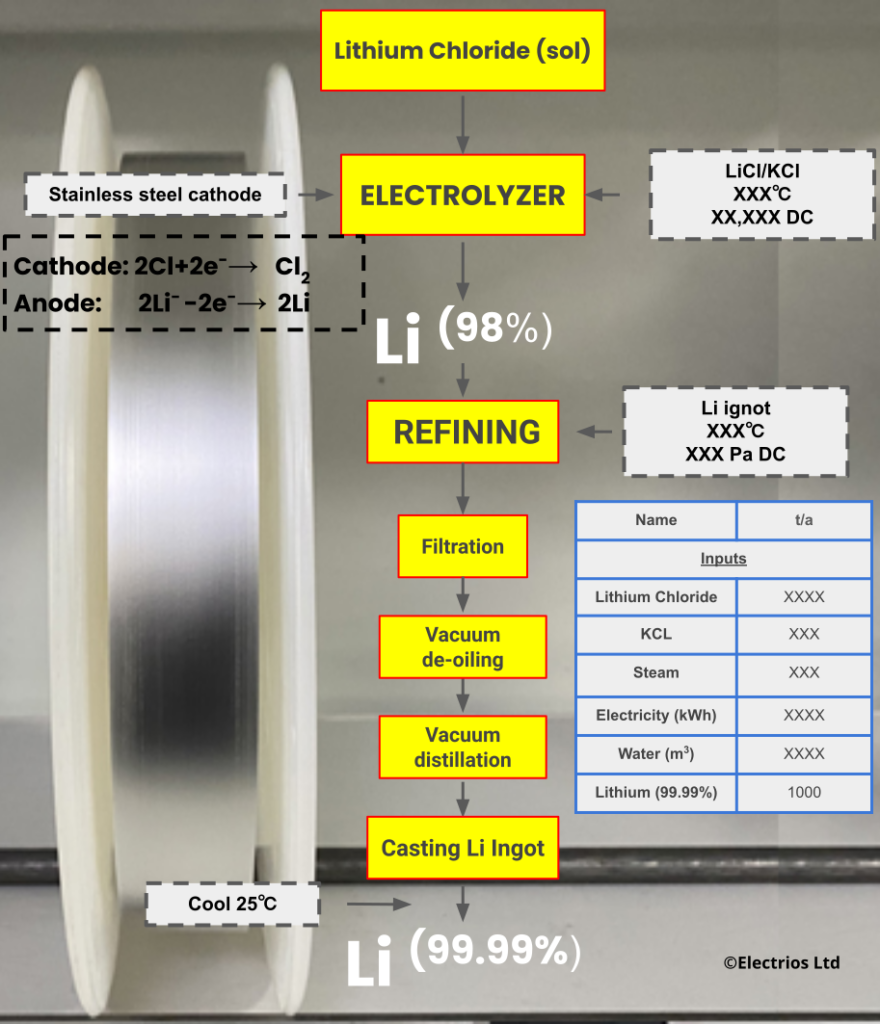
Battery Grade Lithium Metal
1. Electrolysis
- Anhydrous Lithium Chloride: This is the key input for electrolysis. It’s mixed with potassium chloride (KCl) to lower the melting point and improve efficiency.
- Electrolytic Cell: The molten salt mixture is electrolyzed. Lithium metal deposits at the cathode, and chlorine gas is produced at the anode.
- Crude Lithium: This process yields crude lithium with a purity of around 98-99%.
2. Refining and Purification
- Refining: The crude lithium undergoes refining to remove impurities like oxides and nitrides. This may involve vacuum melting, sedimentation, and filtration.
- Vacuum Distillation: To achieve higher purity (up to 99.99%), vacuum distillation is used. This process selectively vaporizes impurities based on their vapor pressures, leaving behind purified lithium.
- Alternative Purification Methods: Fractional crystallization and zone refining are other potential purification methods being explored.
3. Product Forms and Applications
- Diverse Products: Metallic lithium is produced in various forms, including ingots, foils, rods, particles, and alloys.
- Key Applications: These products are used in lithium-ion batteries, pharmaceuticals, alloys for aerospace and other industries.